In this article we will look at an example of how to build docker images and pushing to a Docker registry using the new cross-platform Visual Studio Online Build. As the running example we will take a small Node.js application, push it to a Git repository and have VSO build take over from there.
The goal is to show how to build a docker image and push it to Docker Hub with a Linux build agent. A different machine acting as a web server can then spin up a container from the image a few seconds after.
Prerequisites
Before you get started, make sure you have the following:
- A VSO project
- A Git repository connected to the project (only if you do not use the project repository directly)
- Node.js and npm installed
- A Linux host with Docker, Node.js and npm installed - visit the official Docker guide if you need details on installing Docker
- Alternate credentials configured for an account that the Linux build agent will run as - the account must also be in the Agent Pool Administrators and Agent Pool Service Accounts groups
- A user on Docker Hub and a repository for the application
The Application
The Node.js application, will be made using the Express framework and configured to run on port 8000. Create a project.json file and add express as a dependency:
{
"name": "vso-build-docker-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Node.js app running as a container",
"main": "index.js",
"dependencies": {
"express": ""
},
"author": "Jeppe"
}
Save the following code snippet in a file named index.js:
var express = require('express');
var PORT = 8000;
var app = express();
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello from Docker app!\n');
});
app.listen(PORT);
console.log('Running on port ' + PORT);
Try the application locally, by restoring dependencies and running index.js:
npm install
node index.js
Dockerizing the Application
Before we put our application in a Docker image, I will make a base image that is essentially an ubuntu image with node and npm installed. The Dockerfile for this looks like:
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get -y update
RUN apt-get -y install nodejs
RUN apt-get -y install npm
I have pushed an image built using this Dockerfile to https://hub.docker.com/r/jeppe/ubuntu-node/ that you can use.
Next, create the Dockerfile for the application:
FROM jeppe/ubuntu-node
COPY . /src
RUN cd /src; npm install
EXPOSE 8000
CMD ["nodejs", "/src/index.js"]
The Dockerfile uses the previous image as base image, copies the application into the container in a directory named /src, restores node packages in this directory and runs the web application on port 8000 when starting a container.
If you have Docker installed on your development machine, you can build the image by issuing the following command in the directory:
docker build -t my-node-app .
Finally, push the folder with the Node.js application and Dockerfile to the Git repository.
Creating a Linux Build Agent
With our Node.js application ready to be built as a Docker image, we will set up the Linux host to act as a build agent by installing the agent tooling and connecting it to the VSO account (make sure Docker is installed and running).
The Linux (and OS X) build agent is implemented as a Node.js application. All details regarding setting up a Linux build agent is available on the GitHub repository where you can also view the source code for the build agent.
In a nutshell, run the following in a terminal:
$ sudo npm install vsoagent-installer -g
$ sudo chown -R $USER ~/.npm
$ mkdir ~/agents; cd ~/agents
~/agents$ vsoagent-installer
~/agents$ node agent/vsoagent.js
and follow the configuration of the agent. Use the alternate credentials for the account the agent should run as, and the full URL to your account as server url (e.g. https://myaccount.visualstudio.com).
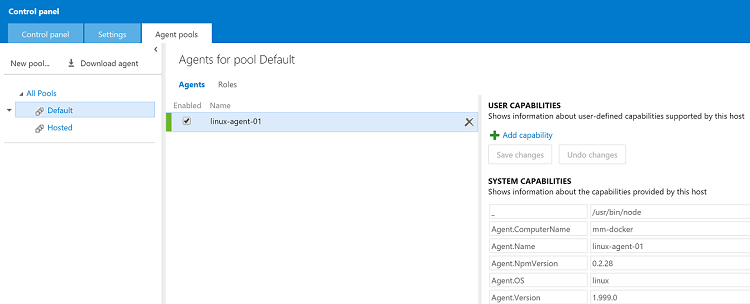
If you navigate to your VSO account settings page and go to the Agent pools tab, you should now find your named Linux build agent in the pool you decided during configuration:
Creating the Build Definition
By now, you should have a Linux build agent running, a Node.js application and a Dockerfile that can be used to build a Docker image containing the application. Let us combine everything and set up the build agent to build the image using the latest version available in the Git repository and pushing it to a repository on Docker Hub.
Currently there are no Docker tasks out of the box, so we will make a simple bash script to run. Add the following build.sh file and push it to the repo:
echo "Building docker image $1 v $2"
docker build -t $1:$2 .
docker push $1:$2
We will control the repository and tag from the build definition and feed those as arguments to the script.
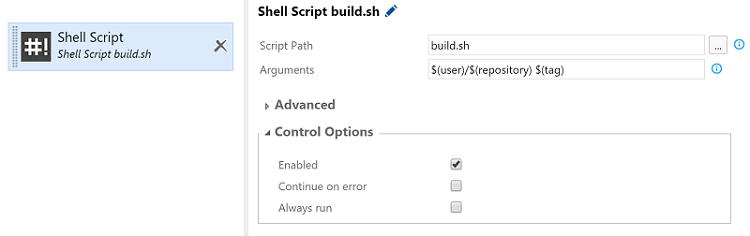
Create an empty build definition and name it e.g. “Build and Push Docker Image”. Add a “Shell Script” task as a build step, and set the following values:
- Script Path: location of the build.sh file in the repository
- Arguments: $(user)/$(repository) $(tag) (remember the space between repository and tag variables)
The build step should now look as follows:
Go to the Variables section and add the following variables (and allow them to be defined at queue time):
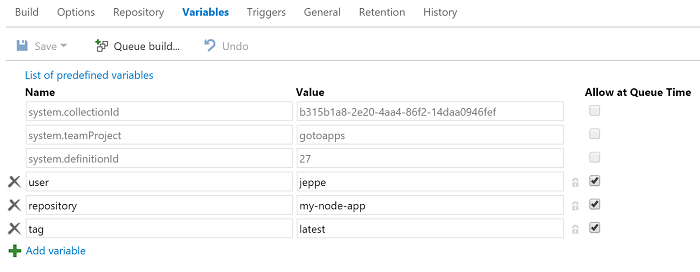 Edit the user and repository value to match your username and repository on Docker Hub - in the screenshot it will build and push the image to my repository jeppe/my-node-app.
Edit the user and repository value to match your username and repository on Docker Hub - in the screenshot it will build and push the image to my repository jeppe/my-node-app.
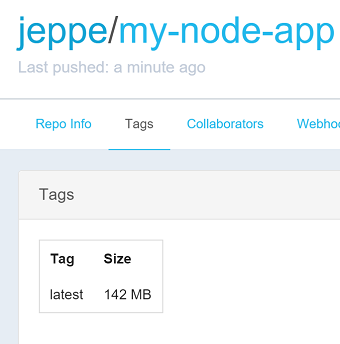
Queue a build to the queue you added the agent to, and you should see the Linux agent start building the image. The first time this will usually take a few minutes. Once completed, you should see it on Docker Hub under tags:
On any other machine with Docker installed you can now run a container and make it serve requests on port 80:
docker run -d -p 80:8000 jeppe/my-node-app
